Glutamate
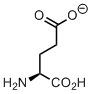 Glutamate is the main metabolite in E. coli constituting almost half of the metabolom in exponentially growing culture.* Why so? Glutamate is a common source of an amino group, and when this is transaminated it is converted to α-ketoglutagate, which can be further transformed in the course of citric acid cycle, and eventually consumed in cataplerotic transformations. Thus, glutamate is a cellular equivalent of an amino group. No wonder the most abundant metabolite is also a component in protein biosynthesis. Proline can be synthesized starting from glutamate.
Glutamate is the main metabolite in E. coli constituting almost half of the metabolom in exponentially growing culture.* Why so? Glutamate is a common source of an amino group, and when this is transaminated it is converted to α-ketoglutagate, which can be further transformed in the course of citric acid cycle, and eventually consumed in cataplerotic transformations. Thus, glutamate is a cellular equivalent of an amino group. No wonder the most abundant metabolite is also a component in protein biosynthesis. Proline can be synthesized starting from glutamate.
What is the function of glutamate in proteins? In catalytic triades as a negatively charged counterpart, on the surface of proteins as an exposed polar residue, in salt bridges along with cationic residues when these are not exposed to the solvent, in coordination of some metal ions, in binding pockets for accommodation of positively charged substrates. There are many places, where versatile glutamate side chain can find a job.
And let’s be honest, who else can make your bouillon so delicious as glutamate does.
Interesting readings:
- *Bennett, B. D., et al. Absolute metabolite concentrations and implied enzyme active site occupancy in Escherichia coli. Nat. Chem. Biol., 5, 2009, 593-599, doi: 10.1038/nchembio.186
>>> Genetic Code <<<
