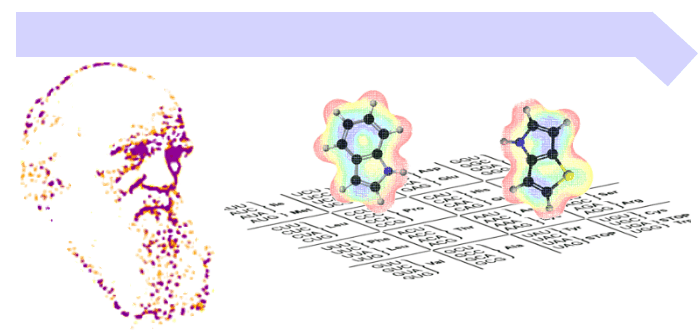
The Genetic Code
Vladimirs Brief History of the Genetic Code
Click here for Vladimirs Brief History of the Genetic Code.
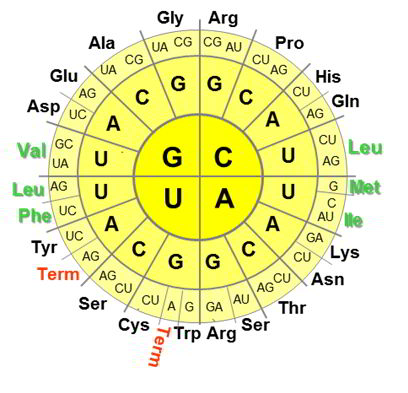
The genetic code is the set of correspondences between the nucleic acid triplets (codons) and amino acids in the primary sequences of ribosomaly produced proteins. The code is universal. With the exception of some small variabilities, this rule prescribes how to decode genes into proteins in all organisms on Earth (and beyond?). For example, every protein synthesis on the ribosome starts with AUG codon, which encodes methionine (Met), CCA will code for proline (Pro), CAC for histidine (His), GUA for valine (Val), etc.
The amino acids encoded by the gene sequences are called coded or canonical amino acid, thus obeying the rule, canon. Each of these amino acids may have its own peculiarities. We have summarized some interesting information and references for the canonical amino acids in dedicated sections. Just click away.
Alanine
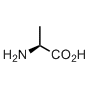
Alanine is not just an amino acid with a smallest side chain. This is also the parent structure for the other 17 amino acids, only proline and glycine have different backbone architecture. The alanine and its derivatives all share common backbone features: there is one hydrogen-bond donor (NH), one hydrogen bond acceptor (C=O), one chiral center (with L-configuration). These features create the world dominated by the α-helix. Alanine is the father of the α-helix, the amino acid with the highest propensity to form this secondary structure.
Because alanine is a generic structure, other amino acids in the protein structure can be substituted with Ala with little to no consequences in the secondary structure fold. This approach is known as the alanine scan. One can one-by-one exchange the amino acids of interest with alanine, and observe the changes in the function. Thereby one can figure out, which side-chain function is involved in the function, whereas the folding will most likely remain unperturbed. The alanine scan is possible due to the fact that other 17 amino acids are built on the alanine core structure, otherwise a substitution would simply ruin the folding.
It is somehow surprising though, that polyalanine does not necessarily fold into an α-helix, but may tend to fold into an extended helix, the polyproline-II helix. This fact has a large significance for our understanding of the unfolded state in proteins.
- Kentsis, A. et al. Unfolded state of polyalanine is a segmented polyproline II helix. Proteins, 55, 2004, 493-501, doi: 10.1002/prot.20051
Arginine
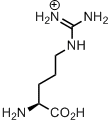
Arginine gives us a positive outlook. There is simply too much negativity in life! Nucleic acids are polyanionic, membrane-forming lipids are in best case zwitter-ionic, but most often negatively charged. Who would be willing to interact with such a problematic company? I’ll tell you: peptides full of arginine.
Arginine is ‘mister positive’ in the protein structures. Well, what’s about lysine? This is positively charged too, but a simple amino-group is more prone to post-translational modifications, and in general lysine is way more susceptible to chemical transformations. Arginine has a positively charged guanidinium ion, and this is a very stable structure. Organic chemists even invented the concept of Y-aromaticity in order to point out its remarkable stability. Guanidinium ion is so stable, that its positive charge can be hardly removed, having pKa around 12.5. Therefore the side chain ensures positive charge of this residue, unless there is metal coordination, which happens also frequently with arginine residues in catalytic centers of enzymes.
In addition to the positive charge stability, the guanidinium structure is also very well fitted for intimate interaction with negatively charged counterparts: phosphates and carboxylates. The stability of resulting salt-bridges is ensured by both electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonds between the interacting fragments:
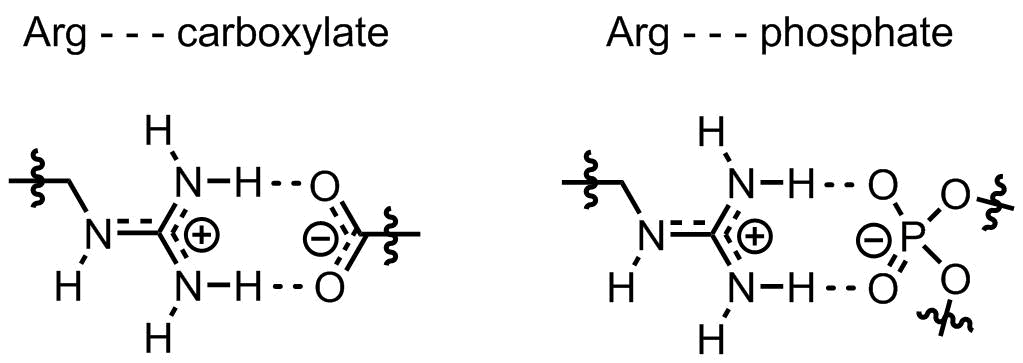
Not surprisingly, arginine-rich sequences can fabulously interact with both, nucleic acids and lipid membranes. For instance, membrane-interactine oligoarginine peptides are well-known cell-penetrating sequences, these are often employed for intracellular delivery of various molecular targets. Or another example would be arginine fork, a special motif of arginines interacting with non-double stranded nucleic acids.
- Woods, A. S. and Ferré, S. Amazing Stability of the Arginine-Phosphate Electrostatic Interaction. J. Proteome Res., 4, 2005, 1397-1402, doi: 10.1021/pr050077s
A salt-bridge between an arginine and a phospo-serine can be as strong as a covalent bond.
- Futaki, S. Oligoarginine vectors for intracellular delivery: Design and cellular-uptake mechanisms. Pept. Sci., 84, 2006, 241-249, doi: 10.1002/bip.20421
The review illustrates design of cell delivery vectors with oligoarginine sequences.
- Xiang, S. and Tong, L. Crystal structures of human and Staphylococcus aureus pyruvate carboxylase and molecular insights into the carboxyltransfer reaction. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 15, 2008, 295-302, doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1393
There is a cluster of tightly bundeled four arginine residues in this structure. This is responsible for the phosphate binding in coenzyme A.
Asparagine
Asparagine got its name from the name of plant asparagus (aka sparrow grass). This is due to the fact that the amnino acid was first isolated from the plant juice. It is not just a coincidence, though. Asparagine is important for plant metabolism due to its high nitrogen content (two N atoms, N/C atom ratio 1:1), while storage and metabolism of nitrogen has a paramount importance for agricultures.
In proteins, asparagine may have different functions. This is a polar residue, which may be placed on a polar exterior of a globular protein. The amino acid side chain has both, hydrogen bond donor (NH2) and acceptor (C=O) places, this can be utilized for hydrogen bonding, or in catalysis. It is also common that the nitrogen atom of asparagine is glycosylated.
- Lea, P. G. et al. Asparagine in plants. Ann, Appl. Biol., 150, 2007, 1-26, doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7348.2006.00104.x
- Imperiali, B. and Rickert, K. W. Conformational implications of asparagine-linked glycosylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 92, 1995, 97-101, doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.1.97
Aspartate
Aspartate is one of the most basic components in the amino acid repertoire, and here is why. First, it is very easy to produce, just one step away from oxaloacetate, the starter of the citric acid cycle. Second, it is an essential component for the synthesis of pyrimidine nucleobases. Every pyrimidine synthesis starts with the attachment of an aspartate to a ribose, and subsequent conversion of the amino acid moiety into a nucleobase is a matter of a few simple steps.
In proteins, aspartate is very common actor in catalytic triads, which involve acid-base transition, for example, lipases or peptidases. A negatively charged side chain of an aspartate is a critical residue, which allows abstractoion of a proton from other catalytic components, such as histidine or serine.
There is a good use of polymeric amino acid, polyaspartate, in industrial settings. Due to a high concentration of the negative charge, this is a good metal coater and water softener, which is fully biodegradable, in contrast to other alternatives (such as polyacrylate).
- Dodson, G. and Wlodamer, A. Catalytic triads and their relatives. Trends Biochem. Sci., 23, 1998, 347-352, doi: 10.1016/S0968-0004(98)01254-7
- Fu, A. and Danial, N. N. Grasping for aspartate in tumour metabolism. Nat. Cell Biol., 20, 2018, 738-739, doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0137-9
- Herring, B. E. et al. Is Aspartate an Excitatory Neurotransmitter? (SPOILER: no) J. Neurosci., 35, 2015, 10168-10171, doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0524-15.2015
Cysteine
Believe it or not, but this was the first amino acid ever discovered by chemists.* Cysteine is most famous for the disulfide bridges it creates. Oxidative conditions allow proximal cysteine residues to form S-S bond, thus ensuring a more stable fold. A classic example is human insulin, where a disulfide bond links together the A- and B-chains making a dimer structure. Linkage to cysteine is also an easiest way to link non-native chemical moieties to a protein. This can be done simply by adding an excess of a thiol reagent that bears the function of interest.
Was disulfide bond the original reason, why cysteine was recruited to the genetic code? Most probably, not. Consider that originally the conditions on the planet were reductive until the great oxygenation event happened after the emergence of photosystem II around 2.5 billion years ago. In the genetic code formation phase the conditions were reductive, therefore disulfide bridges would hardly be possible.
But what’s about metal coordination? Cysteine has the best metal coordinating side chain, especially for transition metals. For example, iron-sulfur clusters are coordinated by cysteines side-chains to form very stable protein-cluster complexes, while other side-chains are involved into a loose coordination to form permissive sites.
One can easily speculate that cysteine-transition metal and direct cysteine-iron complexes played important role under the reductive conditions of the initial life evolution process. Importantly, it is a well-known fact that pre-oxygenated oceans contained a fairly high concentration of dissolved iron (II). Thus, Cys-Fe coupling was probably inevitable, and there are many uses one can imagine for this motif.
Other than this, cysteine is involved in numerous post-translational modification processes, for example, formation of lantionine (thioether bridge) with a dehydroalanine counterpart, or backbone cyclization into a thiazole and more. Glutathione, the second most abundant metabolite in E. coli (after glutamate being the 1st), contains cysteine residue and this maintains the redox potential in the cells. Therefore, after the biosynthesis, a large amount of cysteine is directed towards glutathione synthesis, especially under oxidative stress conditions.
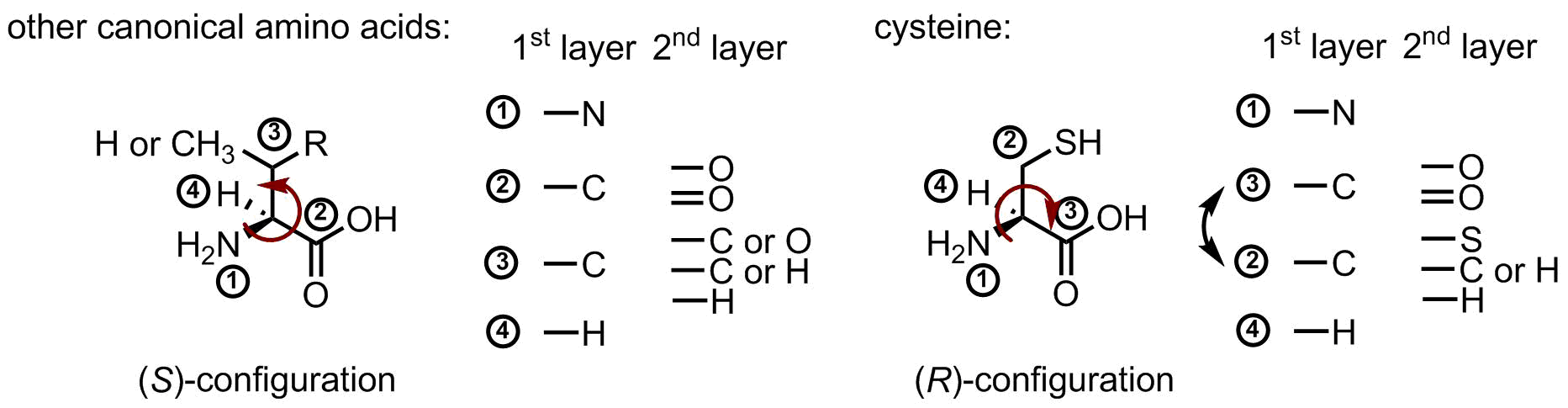
Last fun fact about cysteine, this is the only (R)-amino acid in the canonical repertoire. Below is the figure, which illustrates this. Usually, carboxyl-group has a higher priority than a side chain moiety, because there are three oxygen atoms in the second layer. However, sulfur has a higher atomic number than oxygen, therefore, it swaps the priority, and this changes the name of the configuration:
- Chalker. J. M., et al. Methods for converting cysteine to dehydroalanine on peptides and proteins. Chem. Sci., 2, 2011, 1666-1676, doi: 10.1039/C1SC00185J
Convert cysteine to dehydroalanine and then attach whatever you want.
- Maio, N. and Rouault, T. A. Iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis in mammalian cells: New insights into the molecular mechanisms of cluster delivery. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1853, 2015, 1493-1512, doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.09.009
A recent review about the iron-sulfur clusters.
Glutamate
Glutamate is the main metabolite in E. coli constituting almost half of the metabolom in exponentially growing culture.* Why so? Glutamate is a common source of an amino group, and when this is transaminated it is converted to α-ketoglutagate, which can be further transformed in the course of citric acid cycle, and eventually consumed in cataplerotic transformations. Thus, glutamate is a cellular equivalent of an amino group. No wonder the most abundant metabolite is also a component in protein biosynthesis. Proline can be synthesized starting from glutamate.
What is the function of glutamate in proteins? In catalytic triades as a negatively charged counterpart, on the surface of proteins as an exposed polar residue, in salt bridges along with cationic residues when these are not exposed to the solvent, in coordination of some metal ions, in binding pockets for accommodation of positively charged substrates. There are many places, where versatile glutamate side chain can find a job.
And let’s be honest, who else can make your bouillon so delicious as glutamate does.
- *Bennett, B. D., et al. Absolute metabolite concentrations and implied enzyme active site occupancy in Escherichia coli. Nat. Chem. Biol., 5, 2009, 593-599, doi: 10.1038/nchembio.186
Glutamine
Let’s talk about diseases. Have you ever heard of Huntington disease? The disease named after physician George Hungtington is a neurogenerative disorder, which is genetically programmed. There is one gene, called huntingtin, and this encodes for a polymeric stretch of glutamines (polyQ). Different people have different length. If a person has 35 or below Q, this is safe, and a person shouldn’t be concerned with this. But when the stretch is 36 Q or more, a person shall be aware, that at some point in life, this disease may start to progress. The more Q are in the stretch, the earlier the symptoms will develop.
The actual function of hungtingtin in the cells is still unknown, but the malfunction has been described much better. Longer polyQ stretches are more likely to clump at some point during the lifetime. This statistical process will progress until it will accumulate in amyloids and inclusion bodies, and there will be more and more of these, until neurons will be unable to cope with the cargo, and die as the result. It then makes a great challenge for modern chemistry to develop a treatment of this cruel and deadly disorder.
Other than in proteins, the consumption of glutamine is also enormously elevated in cancer cell metabolism. This brings a hope, that by suppressing some glutamine metabolic pathways, a cancer inhibition would also be possible.
- DeBerardinis, R. J. and Cheng, T. Q's next: the diverse functions of glutamine in metabolism, cell biology and cancer. Oncogene, 29, 2010, 313-324, doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.358
- Wise, D. R. and Thompson, C. B. Glutamine addiction: a new therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci., 35, 2010, 427-433, doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2010.05.003
Two nice reviews on the role of glutamate metabolism in cancer, and possible entries for therapeutics development.
- Kar, K. et al. Critical nucleus size for disease-related polyglutamine aggregation is repeat-length dependent. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 18, 2011, 328-336, doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1992
A model study on the nucleation mechanism in polyQ aggregation.
- Wetzel, R. Physical Chemistry of Polyglutamine: Intriguing Tales of a Monotonous Sequence. J. Mol. Biol., 421, 2012, 466-490, doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.01.030
A nice review on polyQ.
Glycine
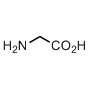
If you like minimalism you choose glycine. It couldn’t get any simple, right? Just two carbon atoms, no chirality… Yet, when people want to minimize influence of a residue, they mutate it to alanine, not glycine, why? This has a reason. Likewise proline, glycine offers a different backbone structure, therefore these three: 1) glycine, 2) proline, 3) all others have each a different map of the allowed conformational states (i.e. Ramachandran plot).
Glycine is special, despite all the minimalism. Due to the absence of chirality and substituents, this can be a helix breaker, and in general, the conformation of this residue are often tricky to decipher.
Overall, there are some regularities in the use of glycine in peptide structures. This residue is very often found on the interfaces between secondary structures. For example, in membrane proteins, the assembly of helical bundles is made through the help of glycine residues, which allow maximally intimate proximity of the helices to one another. The same principle is used in collagen triple helices, where individual stretches are brought into close proximity through the help of glycine residues. No other amino acid can substitute glycine in these cases, and mutations may lead to diseases.
In metabolism, glycine is one of the first components in the purine biosynthesis, the central C4-C5 carbon atoms in purines are inherited from glycine.
- Bowie, J. U. Solving the membrane protein folding problem. Nature, 438, 2005, 581-589, doi: 10.1038/nature04395
General remarks to membrane protein architecture. These are having glycine on interfaces quite often.
- Pace, R. A. et al. Collagen VI glycine mutations: Perturbed assembly and a spectrum of clinical severity. Ann. Neurol., 64, 2008, 294-303, doi: 10.1002/ana.21439
Glycine mutations impair assembly of collagen in the development of muscular dystrophies.
Histidine
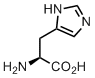
The king of biocatalysis. This amino acid is the most costly when it comes to metabolic biosynthesis. Yet, it is worth the investments. The acid-base transition for the imidazole side chain occurs at the pH close to neutral values, and due to this fact, His residue is very common in catalytic triades. Proteases, lipases and many other enzymes require His for proton shuttling during the catalytic cycle.
Other important function of this side chain is ‘soft’ metal coordination, for instance, heme coordination usually involves either Met sulfur of His imidazole as an axial ligand, while the other axial position is available for catalysis. The metal coordination feature is also exploited in so-called histidine tags, a bunch of consecutive His residues for affinity chromatography on nickel (II) based stationary phase.
- Beiboer, S. H. W. et al. Incorporation of an unnatural amino acid in the active site of porcine pancreatic phospholipase A2. Substitution of histidine by l,2,4-triazole-3-alanine yields an enzyme with high activity at acidic pH. Protein Eng., 9, 1996, 345-352, doi: 10.1093/protein/9.4.345
The title speaks by itself. In comparison to imidazole, triazole has a different protonation profile, thus allowing the shift of the pH optimum to a different pH value in porcine pancreas phospholipase A2.
- Xiao, H. et al. Genetic Incorporation of Histidine Derivatives Using an Engineered Pyrrolysyl-tRNA Synthetase. ACS Chem. Biol., 9, 2014, 1092-1096, doi: 10.1021/cb500032c
In this paper, they develop an orthogonal pair to incorporate various histidine derivatives into proteins.
- Green, A. P. et al. A Chemically Programmed Proximal Ligand Enhances the Catalytic Properties of a Heme Enzyme. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 138, 2016, 11344-11352, doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b07029
The paper is concerned with the reasons for the Asp-His placement below the heme cofactor in a peroxidase enzyme. The authors replaced the histidine with N-methyl histidine, and found that the enzyme performs even better than before. This spectacular finding is very well explained in the discussion section.
Isoleucine
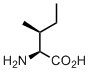
Isoleucine is among the most neglected amino acids in the genetic code repertoire. Often people say: why there is iso-leucine, when there is alsready leucine, isn’t isomeric amino acid obsolete? We certainly cannot agree with this kind of argument, and here is why. Isoleicine and leucine are common names for the amino acids, but these are not what is called systematic names. Systematic names are usually given in organic chemistry in order to designate a chemical structure with its unique and unambiguous textual equivalent. According to these rules isoleucine should be called (2S,3S)-2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid, whereas leucine’s name will be (2S)-2-amino-4-methylpentanoic acid. Both structures have almost identical names; although they are actually isomeric to each other, there is no more ‘iso’, both names are just different. It is thus fully ambiguous which amino acid is considered the ‘original’, and which one is the ‘other isomer’. We could also say, that isoleucine is isoisoleucine.
In fact, both amino acids have equal rights to be fully competent in fulfilling usual tasks of hydrophobic amino acids: cause hydrophobic collapse in globular proteins, and form hydrophobic exterior of membrane immersed sections in membrane proteins.
Let’s look at another example. There are two main toxins from death cap mushroom, amanitin and phalloidin. Both are bicyclic short peptides with very similar type of structures. There is one interesting difference though. Phalloidin structure has dihydroxy-leucine as one of the residues, while amanitin has dihydroxy-iso-leucine. These peptides are very nasty toxins, which cause much troubles for people and animals, who get poisoned by this deadly mushroom. There is derivative of one amino acid in one case, and another - in the other. Interestingly, it has been found that dihydroxy-leucine moiety is not very critical in the activity mode of phalloidin toxin, whereas the dihydroxy-iso-leucine is involved in the mode of action of amanitin.
This example illustrates how nature manipulates with these amino acid residues in order to create desired activity and selectivity of the specific natural products. Leucine and isoleucine are both important, and their choice in one or another structural context can have a difference in fine tuning of the interaction with the surrounding. After all, we should face the fact that almost all types of side-chain functions are not unique: there are two positively charged amino acids (Arg, Lys), negatively charged - also two (Asp, Glu), aromatic - three (Phe, Tyr, Trp), two - with hydroxyl-groups (Ser, Thr), two amides (Asn, Gln) etc. Thus, it should not surprise us that there are few aliphatic hydrophobic amino acids in the genetic code set.
There is no general rule, how to choose between Leu and Ile for better performance in a protein structure. However, there are arguments which indicate that Leu may be slightly better hydrophobic amino acid for making hydrophobic face in water-exposed -helices, whereas, Ile - may be slightly better doing the same job in lipid-exposed transmembrane helices. This is due to the fact that Ile side-chain is closed to the backbone, and may shield it better from the lipid. In contrast, Leu has a better -helical propensity in water, and there it may be critical for the stability of the helix.
Another peculiarity of isoleucine is the fact that the amino acid has a second chiral center, a chiral center in the side chain. Hydrophobic surfaces formed by isoleucine should be highly chiral. Perhaps, in the future, we’ll get more information, how to make use of this feature.
- Deber, C. M. and Stone, T. A. Relative role(s) of leucine versus isoleucine in the folding of membrane proteins. Peptide Sci., 111, 2019, e24075, doi: 10.1002/pep2.24075
- Li, S.-C. and Deber, C. M. A measure of helical propensity for amino acids in membrane environments. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 1, 1994, 368-373, doi: 10.1038/nsb0694-368
Leucine
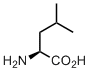
Leucine takes us to the membrane. And it deserves very loud applauses. We now take it for granted, but originally, entering the membrane hydrophobic core for life was like… like for us would be colonizing Moon or Mars. Leucine made it possible, isn’t it amazing?
We now enjoy a large variety of membrane proteins, which are absolutely essential for sustaining life. It is also the membrane, which allows cells create chemiosmotic gradients, and subsequently, generate ATP. The membrane proteins basically define what goes in, and what goes out, they sort what should be kept and what should be discarded, released, produced or exchanged by a cell. The cell itself is defined through the membrane and membrane proteins. But how did nature transverse this medium in the first place, how did it overcome the hydrophobic core, which is essentially an oil? Nucleic acids are too polar to enter it. Peptides are polar too, owning to the high polarity of the amide-based backbone. Yet, nature entered the membrane with the α-helix due to the recruitment of leucine to the canonical repertoire.
The structure of the leucine side-chain starts with a CH2-group, and this rather compact linker allows packing of this residue in the crowded context of an α-helix, full of other side-chains. Next, there is an iso-propyl attached to the linker, and this moiety forms a hydrophobic exterior. That’s it. You don’t even need a poly-leucine sequence, just leucine-rich shall be enough to form a hydrophobic α-helix.
Next effect occurs when this comes into the membrane, into the hydrophobic core, which is non-polar. This environment has a very little dielectric constant (ε ~ 2) in comparison to well insulating water (ε ~ 80), thereby strengthening the polar interactions of the backbone. Not only the α-helix becomes compatible with a hydrophobic medium, but also this structure becomes enormously strong.
Integral membrane proteins are most commonly made by motifs called α-bundles, and these allow formation of ion-channels, receptors, transporters and more, all possible functions.
- Pace, C. N. and Scholtz, J. M. A Helix Propensity Scale Based on Experimental Studies of Peptides and Proteins. Biophys. J., 75, 1998, 422-427, doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77529-0
A useful survey of α-helix propensity scales for amino acid..
- Holt, A. and Killian, J. A. Orientation and dynamics of transmembrane peptides: the power of simple models. Eur. Biophys. J., 39, 2010, 609-621, doi: 10.1007/s00249-009-0567-1
A recent review about the iron-sulfur clusters..
WALP and KALP peptides are common biophysical models for studying transmembrane helices. These are having repetitive (LeuAla)n stretches as the hydrophobic core spanning sequences. A review discusses some findings made with these models in a recent decade. .
- Lee, B. D. et al. Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) as a potential therapeutic target in Parkinson's disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 33, 2012, 365-373, doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2012.04.001
Leucine-rich repeat is a common motif in protein-protein interactions, related to a variety of diseases. An example is inherited Parkinson disease, and the review describes possible development of therapeutics targeting this motif.
Lysine
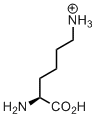
Lysine is the only canonical amino acid, which bears an amino group. This is a must-have moiety when designing proteins, for example, as a site for ligations. Strong covalent ligations can be made via an amide bond with a carboxyl-group reagent, likewise in biotin attachment forming biocitin. More loose attachment can be made via a Schiff-base with an aldehyde or ketone counterpart, for instance, when pyridoxal-5-phosphate is harbored by an enzyme the aldehyde group is attached to a lysine amino-group. Attachment of a carbon dioxide molecule creates carboxy-lysine, an important general base in enzymatic transformations.
No wonder that lysine (along with cysteine) is the most common target for man-made so-called ‘bioorthogonal’ attachment of various molecules. Cross-linking mass spectrometry, a method to track interacting protein-protein interactions, relies primarily on covalent cross-linking of lysine residues at interacting interfaces.
There is an ample amount of other lysine-specific chemical aspects. For example, lysine is involved in numerous catalytic triads promoting protonation-deprotonation, nucleophilic mechanisms and others. There is a rich post-translational modification chemistry done with this side chain, for instance, in lysine-rich DNA-packing histone proteins.
But let’s discuss one interesting chemical aspect of the lysine, its length. Why is it so important that lysine has four methylene units between the amino-group and the backbone?
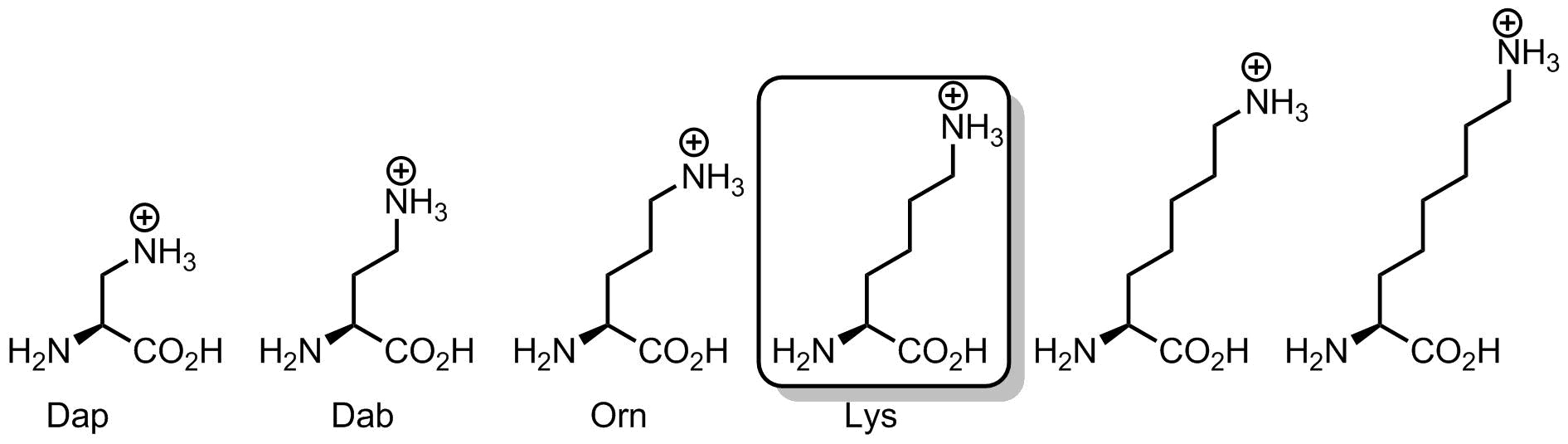
Let’s see whether the linker can be shorter. First, we can exclude diamino-butyric acid (Dab) from occurrence in translation process due to important chemical reasons. This amino acid, when attached onto a tRNA in a form of an amino acyl-tRNA ester would most likely form intramolecular cyclization product, thus, it would cleave itself and then leave in the form of an amino-pyrrolidone. The anomaly of 5-membered rings is very familiar in organic chemistry, and basically, whenever a nucleophilic reaction leads to a 5-membered ring, the likelihood of its occurrence becomes enormous. The same reason explains why homoserine translation would also be impossible.
What if linker is just one carbon, and the amino acid is diaminopropionic acid (Dap). Here a positively-charged ammonium group would be placed very close to the backbone. However, the problem is that this group would require an extensive solvation by water. Thus, solvation shell would most likely interfere with the neighboring residues in a context of a compact helical structure, such as α-helix. Another outcome, is that surrounded by other side chains, the ammonium group would hardly be accessible for chemical reactions, such as Schiff-base formation and others. To make it more accessible, yet well solvated, one should elongate the linker to allow maximal emergence of the terminal nitrogen atom into the solvent. Like a toy balloon or a kite. The higher it rises, the more solvated and accessible it becomes.
How high can it go? Remember, that the linker in an olygomethylene (CH2)n, and this is a hydrophobic chain. We cannot increase its length forever, because at some point it would start to collapse with the neighboring hydrophobic side chains and with itself. Therefore, four methylene units is probably the optimal distance at which these different considerations find a compromise. Actually, people often forget that lysine side-chain is quite hydrophobic due to its length, and this is the ammonium charge, which makes it hydrophilic eventually. However, when the charge is eliminated by N-acetylation or in N-Boc lysine, the amino acid can become fairly hydrophobic.
- Padmanabhan, S. et al. Helix propensities of basic amino acids increase with the length of the side-chain. J. Mol. Biol., 257, 1996, 726-734, doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0197
The paper addressed the helix propensity of lysine homologs in a context of Lys(Ala)4-based repetitive peptide structures.
- Rappsilber, J. The beginning of a beautiful friendship: Cross-linking/mass spectrometry and modelling of proteins and multi-protein complexes. J. Struct. Biol., 173, 2011, 530-540, doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2010.10.014
The perspective explains how tethering interacting surfaces together can help to identify new protein-protein interaction networks. Lysine is the key amino acid, since it’s abundant on the surface, and can be easily ligated and cross-linked.
- Koniev, O. and Wagner, A. Developments and recent advancements in the field of endogenous amino acid selective bond forming reactions for bioconjugation. Chem. Soc. Rev., 44, 2015, 5495-5551, doi: 10.1039/C5CS00048C
A recent review on biorthogonal chemistry on proteins. Lysine ligations are regarded as “the oldest and most versatile techniques for protein conjugation”.
- Maier, G. P. et al. BIOLOGICAL ADHESIVES. Adaptive synergy between catechol and lysine promotes wet adhesion by surface salt displacement. Science, 349, 2015, 628-632, doi: 10.1126/science.aab0556
How to make a good adhesive? The paper demonstrates that combination of a lysine positive charge and a catechol leads to a dramatic synergetic enhancement of adhesive properties.
Methionine
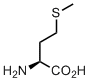
Methionine has a snake side chain. Or shall we call it a sneak? This linear non-branched hydrophobic side-chain can easily sneak into hydrophobic pockets of different shapes. Therefore, if you want to accommodate a hydrophobic substrate with a tricky shape, you’d probably take methionine.
A methionine rich domain in signal-recognition particle (SRP) complex is the one responsible for recognition of hydrophobic sequences (i.e. the signal) emerging from the ribosome. Thus, it is essential for the SRP-mediated targeting to the translocon.
Although, methionine is an excellent hydrophobic amino acid, it has what the call in IT a critical vulnerability: it is prone to oxidation. When sulfur is oxidized by reactive oxygen species, this creates first a sulfoxide and then sulfone. Both are polar. Therefore, oxidation of methionine is a detrimental process for proteins having methionine side chain in the hydrophobic core. Reversal of the methionine oxidation is a serious task undertaken by methionine sulfoxide reductases. If these enzymes forget to reduce the side-chain when it’s still a sulfoxide, beware, next oxidation will make a sulfone, and the transition will be settled irreversible.
Interestingly, participation in translation is not the main role of methionine in living cells. The main function of this amino acid is formation of S-adenosyl-methionine (known as SAM or AdoMet). This key metabolite is involved in a variety of processes: radical chemistry, C1-metabolism, methylation reactions (e.g. DNA methylation) and polyamine biosynthesis.
Somehow mysterious is the fact that every protein sequence starts with a methionine (N-formyl methionine in bacteria), i.e. methionine codon AUG is also the start codon. The reason for this is still unknown, though.
- Wild, K., et al. SRP meets the ribosome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 11, 2004, 1049-1053, doi: 10.1038/nsmb853
The structural model of SRP-mediated ribosome-nascent chain complex targeting to the translocon. The first and key step is the interaction of the C-terminal methionine-rich domain with the N-terminal hydrophobic protein stretch emerging from the ribosome.
- Moskovitz, J. Methionine sulfoxide reductases: ubiquitous enzymes involved in antioxidant defense, protein regulation, and prevention of aging-associated diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta,, 1703, 2005, 213-219, doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2004.09.003
A review of the methionine sulfoxide reductases, important cellular antioxydants.
- Laurino, P. and Tawfik, D. S. Spontaneous Emergence of S-Adenosylmethionine and the Evolution of Methylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 56, 2017, 343-345, doi: 10.1002/anie.201609615
Prebiotic chemistry. The paper demonstrates spontaneous emergence of SAM, an important cellular metabolite, and describes conditions for this process.
Phenylalanine
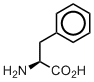
In the genetic code set, phenylalanine is an amino acid with the most hydrophobic side chain. However, this hydrophobicity is different. The classical hydrophobic amino acids, Val, Leu, Ile, have their side chain branched and therefore protruding in different directions. The side chain in Phe is a single benzene ring, which is flat. Therefore, Phe is hydrophobic, but the topology of the side chain is drastically different. As the result, Phe has hydrophobic, but also compact side chain, which may occupy specific places in hydrophobic cores of proteins.
The π-system created by the benzene ring may have a special use in interaction of proteins with other species. This is called π-stacking interaction. Although, Phe is usually not as good in this interaction as Tyr or Trp, it can still donate some of the π-density to counterparts with reduced electron density. This could be for example, cations, nucleobases, or specific enzyme substrates.
Finally, Phe is a precursor to tyrosine, and a number of neurotransmitter and hormones, adrenaline, dopamine, phenetylamine, etc. Phenylalanine is a parent structure in diverse chemical pathways. Therefore, it is difficult to underestimate importance of this simple basic structure.
- Blau, N. Genetics of Phenylketonuria: Then and Now. Hum. Mutat., 37, 2016, 508-515, doi: 10.1002/humu.22980
- Wang, F. and Feng, C.-L. Metal-Ion-Mediated Supramolecular Chirality of l-Phenylalanine Based Hydrogels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 5655-5659, doi: 10.1002/anie.201800251
Proline
Proline is a mysterious amino acid. With proline you basically should forget everything what you’ve learned about the amino acids, because this chap won’t fit in any common category.
On the one hand, the structure contains only 5 carbon atoms with no side chain functional group, looks easy, right? However, on the other hand, this is the only secondary amino acid in the canonical repertoire (sometimes people call it an imino acid, but this is wrong). The endocyclic amino-group restricts the set of allowed backbone conformations. In addition, peptidyl-prolyl linkages are tertiary amide bonds, prone to cis-trans isomerization issues. Let’s illustrate this argument with the help of a figure:
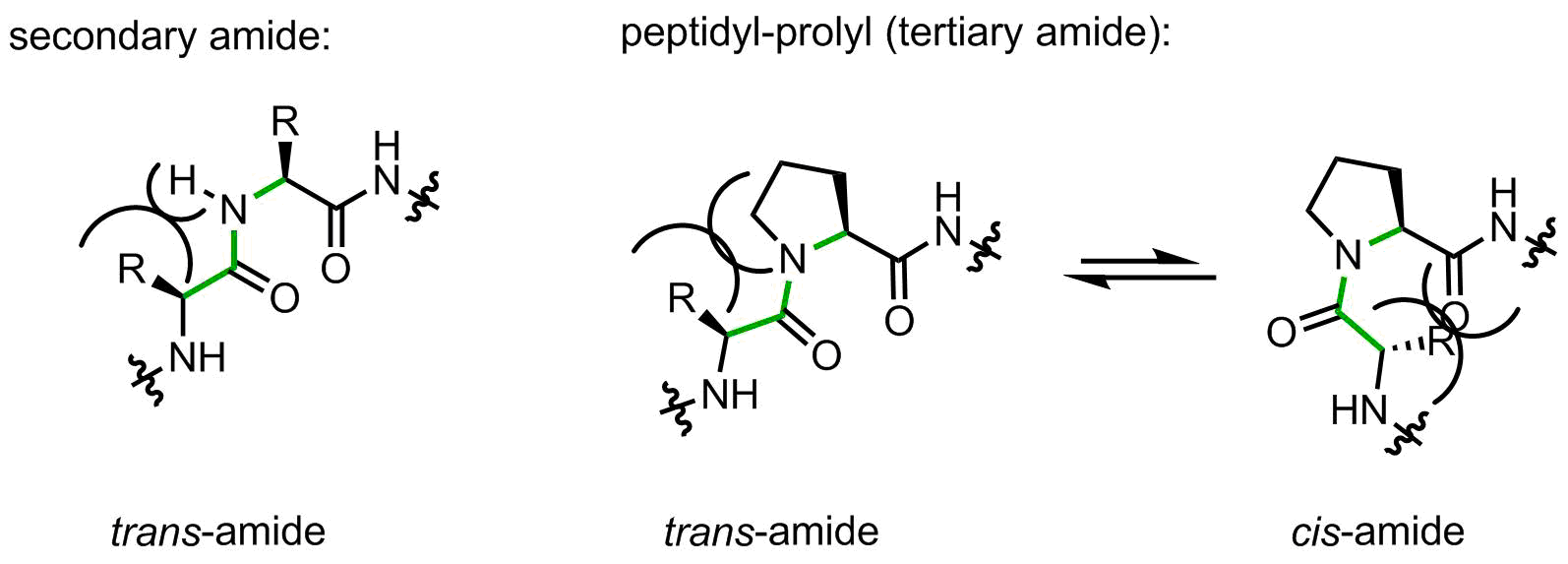
When a peptide bond is made by a secondary amide, the small substituent (hydrogen atom) is placed on the same side as the large upstream peptide fragment, thus making a trans-amide favorable. Indeed, in secondary amides the trans/cis preference is usually > 100:1.
Proline forms a tertiary amide. Now the upstream peptidyl moiety is placed next to the CH2-group, which is notably larger. The amide can flip to the cis-amide conformation with a little loss in energy. In peptidyl-prolyl fragments, the intrinsic preference towards trans-amide is reduced to 2-10:1 depending from the amino acid context, this means a very little intrinsic preference.
The flipping of the peptidyl-prolyl fragment from cis to trans conformation and back is well known in protein biophysics and biochemistry. Because the amide bond rotation is a slow process, this phenomenon can be considered as molecular timer in folding and in signaling. In nature, the correct positioning of some peptidyl-prolyl amides is facilitated by little helpers, chaperones called peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerases.
Another famous feature of peptidyl-prolyl fragments is the lack of NH, which makes them unable to donate a backbone H-bond. This feature along with the backbone conformation restricted by the 5-membered ring make proline a breaker of common α-helices and β-sheets. The lack of NH make proline residues invisible for many biophysical methods based on NMR. The red-shifted light absorption profile of the tertiary amide also complicates UV-based conformational analyses, for example circular dichroism.
Oligomeric (Pro)n and proline-rich fragments forms a special type of fold called polyproline helix, with the polyproline-II helix forming preferentially. Ribosomal translation of proline into proteins is known to be a slow process for both, P- and A-sites. Sequences with 2-3 proline residues induce ribosome stalling, requiring a special elongation factor to alleviate the translation process (called elongation factor P, EF-P). In organic chemistry, proline’s famous property is its prominent organocatalytic activity in condensation reactions.
The classical dual hydrophobic/hydrophilic classification of amino acids fails completely when it comes to proline. Please, be aware that proline can be completely water exposed or be buried into a hydrophobic core of a protein. Both are possible depending from the context.
- Fischer, G. Chemical aspects of peptide bond isomerization. Chem. Soc. Rev., 29, 2000, 119-127, doi: 10.1039/A803742F
Classical review for the cis-trans isomerism around peptidyl-prolyl, mechanisms of the process and influence of the context amino acids.
- Kay, B. K. et al. The importance of being proline: the interaction of proline-rich motifs in signaling proteins with their cognate domains. FASEB J., 14, 2000, 231-241, doi: 10.1096/fasebj.14.2.231
This is an interesting discussion on how proline-rich fragments and polyproline conformation are involved in protein-protein interactions.
- Zondlo, N. Aromatic–Proline Interactions: Electronically Tunable CH/π Interactions. Acc. Chem. Res., 46, 2013, 1039-1049, doi: 10.1021/ar300087y
The paper illustrates molecular principles of the aromatic side chain – proline interactions using molecular models.
- Green, R. Getting Past Polyproline Pauses. Science, 339, 2013, 38-39, doi: 10.1126/science.1233338
Rachel Green explains the phenomenon of ribosome stalling on oligoproline stretches and how the ribosomes are rescued by EF-P. The discovery of oligoproline stalling was made independently by two groups from Göttingen (M. Rodnina) and Munich (K Jung, D. Wilson).
- Kubyshkin, V and Budisa, N. Amide rotation trajectories probed by symmetry. Org. Biomol. Chem., 15, 2017, 6764-6772, doi: 10.1039/C7OB01421J
Our recent molecular model, which illustrates how peptidyl-prolyl rotation should proceed.
- Dobitz, S. et al. Oligoprolines as Molecular Entities for Controlling Distance in Biological and Material Sciences. Acc. Chem. Res., 50, 2017, 2420-2428, doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00340
A recent review of the use of oligomeric proline sequences in material science and drug design applications.
Serine
Are you looking for a residue to modify? Well, you have to try serine. This amino acid is a champ when it comes to modifications. First, it is clearly hydrophilic, therefore, it can be exposed to the solvent, and then an enzyme can easily access it and place an attachment on the hydroxyl-group: phosphate, sugar moiety, acetyl, etc. Protein kinanses most commonly phosphorylate serine residues, while phosphatases dephosphorylate them, and both processes are often running at the same time. If you think, this is a waste of precious ATP, you’ll be wrong. Phosporylation-dephosporylation of serine and threonine is one of the regulatory mechanisms in eukaryotic cells, thus making them able to react to changing conditions by reducing the activity of enzymes, rather than switching them off completely. For example, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex can have a few phosphorylation sites, which would reduce the activity of the enzyme, when there is enough ATP, and no pyruvate shall be burned in the TCA cycle. Phosposylation-dephosphorylation is also involved in genetic regulation, and malfunction of this process can promote cancer.
Role in catalysis. Well, this is very important function of this amino acid. Many catalytic triades employ serine as a nucleophilic end of a catalytic cascade. Likewise, acetyl-choline esterase, one of the most efficient enzymes, it is responsible for rapid degradation of acetylcholine neurotransmitter in sinapses, after neuronic signal has been transmitted. The nucleophile here is a serine side chain. Blocking of this serine is targeted by chemical weapons as well as agrochemical insecticides. Would you like to try some Russian tea from Salisbury? The reason, why sarin, soman and other frequently used organophosphates are such efficient weapons, is due to their covalent binding to the catalytic serine in acetylcholinesterase. Although, this is only one example, many enzymes cannot function without catalytic serine, and its function can rarely be overtaken by threonine, since threonine has a lower degree of side-chain rotational freedom.
Participation in translation and protein build-up is not a main function of serine in cells, while its major role is C1-metabolism. Conversion of serine to glycine releases a methylene-tetrahydropholate, which is a source of C1-unit in many cellular processes, such as production of thymidine or methionine. Tryptophan is synthesizes by condensing serine with an indole. Biosynthesis of cysteine also requires serine. Selenocysteine is a special canonical amino acid, which is made pre-translationaly from serine: because free selenocusteine would quickly degrade in the cytosol, first, a tRNA-loaded serine side chain is converted by a special enzyme into selenocysteine residue, and then this is brought on the ribosome, where the amino acid is incorporated into proteins.
Overall, serine is highly abundant and versatile amino acid. But beware of its evil twin brother, D-serine, which may inhibit cellular growth, or damage kidneys.
- Krug, A. W. et al. Why is D-serine nephrotoxic and a-aminoisobutyric acid protective? Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol., 293, 2007, F382-F390, doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00441.2006
The title speaks it all. The study addresses toxicity of serine, and has an interesting introduction.
- Ekici, O. D. et al. Unconventional serine proteases: Variations on the catalytic Ser/His/Asp triad configuration. Protein Sci., 17, 2008, 2023-2037, doi: 10.1110/ps.035436.108
The review illustrates differences in catalytic triads of serine proteases.
- Endicott et al. The structural basis for control of eukaryotic protein kinases. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 81, 2012, 587-613, doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-052410-090317
The review provides an overview of protein kinases, their structures, activation and general aspects.
- Lizcano, A. et al. A role for glycosylated serine-rich repeat proteins in Gram-positive bacterial pathogenesis. Mol. Oral. Microbiol., 27, 2012, 257-269, doi: 10.1111/j.2041-1014.2012.00653.x
The review discusses involvement of serine-rich repeats in bacterial pathogenicity.
Threonine
Threonine is a Janus amino acid. Its side chain bears both methyl-group and a hydroxyl-group. In solution, this combination is hardly spectacular. However, in a context of a protein, turning of the side chain by its polar or nonpolar face can make a dramatic difference for packing or substrate accommodation.
One more thing is notable about threonine. This is the only D-structure in the canonical amino acid repertoire. Not a D-amino acid, though, it’s a D-sugar. Due to the hydroxyl-group threonine can be classified both as an amino acid and as sugar, and if we name it as a sugar, then we should look at the stereocenter at the bottom of the structure, and this indicates a D-configuration, voila:
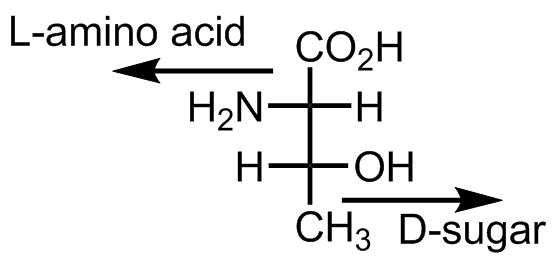
- Kiselev et al. Why Does Threonine, and Not Serine, Function as the Active Site Nucleophile in Proteasomes? J. Biol. Chem., 275, 2000, 14831-14837, doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.20.14831
The paper speculates about the choice of threonine in threonine protease, and shows that switch of Thr to Ser changes the kinetic mode of proteolytic degradation.
- Brister, M. A. et al. OGlcNAcylation and Phosphorylation Have Opposing Structural Effects in tau: Phosphothreonine Induces Particular Conformational Order. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 136, 2014, 3803-3816, doi: 10.1021/ja407156m
The paper illustrates some differences between post-translational modifications (glycosulation and phosphorylation) on threonine and serine. Basically, in the case of threonine the conformational impact is stronger.
- Burnett, J. C et al. A threonine turnstile defines a dynamic amphiphilic binding motif in the AAA ATPase p97 allosteric binding site. Org. Biomol. Chem., 15, 2017, 4096-4114, doi: 10.1039/C7OB00526A
This is a very notable paper, which shows that turning of two gating threonine side chains can help to accommodate both hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups in an inhibitor molecule.
Tryptophan
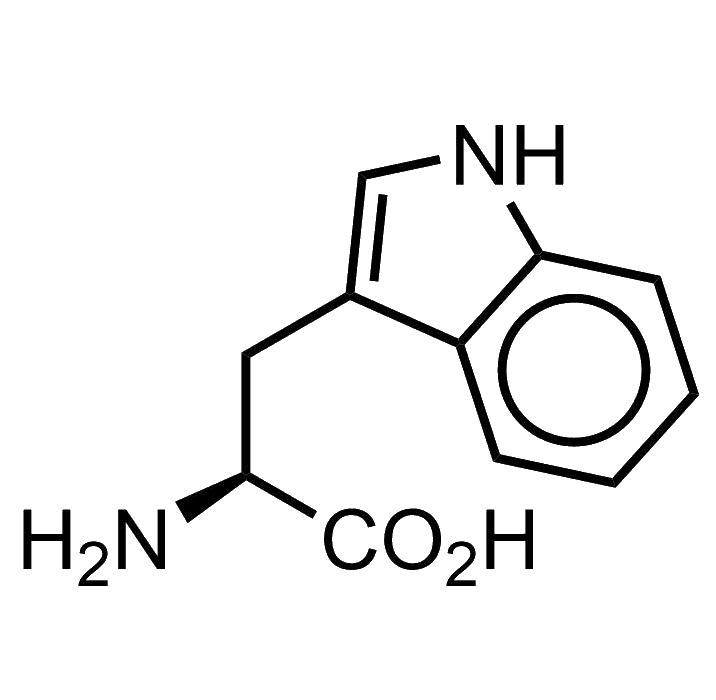
Tryptophan bears an indole as its side chain. This chemical moiety is a very versatile heterocycle, and there are many indole derivatives in biochemistry: secondary metabolites, antibiotics, toxins, drugs, you name it… LSD, well, yes, LSD too is an indole derivative.
But what is the role of tryptophan when the amino acid lands into proteins? First, we can notice that indole is a large aromatic fragment, which can be hydrophobic. However, the presence the heterocyclic component creates a few dipole axes, and this creates a fairly decent overall dipolar moment of the molecule (2.2 Debye). The final outcome is that indole becomes amphiphilic, and therefore can occupy positions at interfaces between environments with different polarities. Classical example is the lipid membrane, where tryptophan often serves as an anchoring residue, with the indole penetrating between polar head-groups and fatty tails. Thus, in transmembrane helices tryptophan side chain would be responsible for correct positioning of the helix in the membrane.
There is another reason, why tryptophan residue becomes membrane-anchoring. If you look at the structure of the membrane, the lipid tail segment is fully packed with the fatty acid tails, while the head-groups are organized by various fragments like phosphacholine, phosphainositol, etc,, all these are also bulky. There is always a glycerol structure linking these two together, and this junction point becomes quite thin. As the result, the membrane structure forms a small region with underpressure at the tail/head-group interface. This vacuum section can easily suck in amino acid side chains with flat shape, such as aromatic structures. Since indole is also amphiphilic, this becomes an ideal place to harbor this side chain. Phenylalanine and tyrosine cannot overtake this job so easily, since these aromatics are too hydrophobic to be placed at an interface position. Tryptophan offers the best solution.
Let’s mention rich variety of post-translational modification chemistry with tryptophan, for example: hydroxylation, halogenation, geranylation, cyclization, etc. The main toxins of the red cap and death cap mushrooms, amanitins and phalloidins, have a cysteine-tryptophan side-chain-side-chain bridges, important for maintaining their evil bicyclic structures. In addition to the chemical versatility, tryptophan is extensively used in biochemical assays and biophysical studies due to its UV-absorption and fluorescence features.
Is tryptophan essential for life? Well… no. In 2015 we demonstrated that the function of tryptophan can be overtaken by thienopyrrole-alanine, and that the amino acid exchange to its analogue can be made globally in E. coli cells in all 21k positions in the proteome. Of course, E. coli was somehow an easy target, since there is no secondary metabolism or post-translational modifications with tryptophan in this organism. However, overall it demonstrates that on organism can live even when we exchange one amino acid by another, which is pretty spectacular.
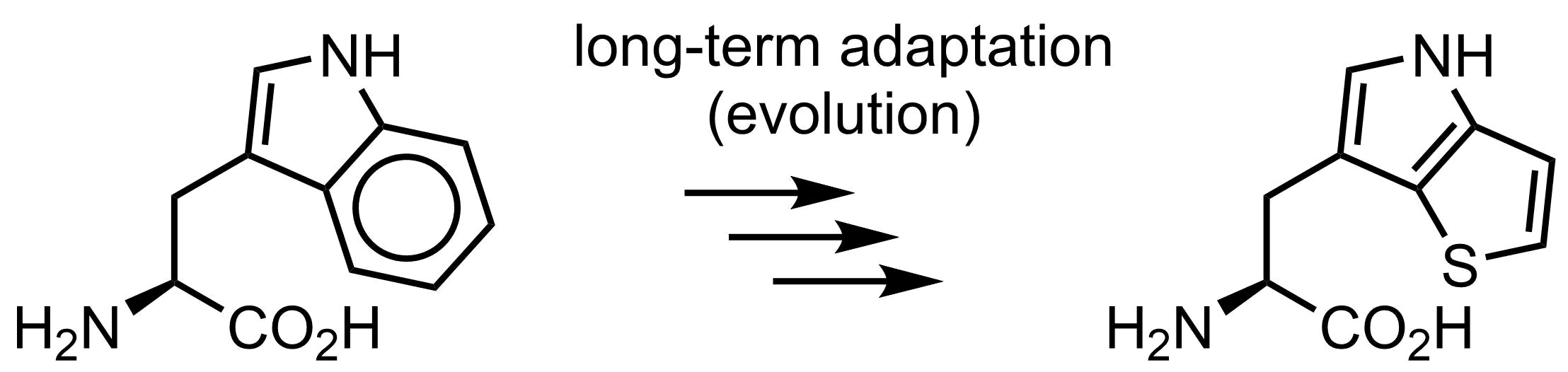
Why is then tryptophan structure in the genetic code? There should be reasons, and we in our lab have some discussions and ideas how this happened.
- Okada, M. et al. Posttranslational isoprenylation of tryptophan in bacteria. Beilstein J. Org. Chem., 13, 2017, 338-346, doi: 10.3762/bjoc.13.37
A recent review on post-translational isoprenylation of tryptophan, mainly coming from B. subtilis.
- Hoesl, M. G. et al. Chemical Evolution of a Bacterial Proteome. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 54, 2015, 10030-10034, doi: 10.1002/anie.201502868
Evolution experiment, where tryptophan was completely exchanged to thienopyrrolylalanine in E. coli.
- Matinkhoo, K. et al. Synthesis of the Death-Cap Mushroom Toxin α-Amanitin. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 140, 2018, 6513-6517, doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b12698
First chemical synthesis of the main toxin of the death cap mushroom. The molecule contains a side-chain macrocycle formed by Trp and Cys residues.
Tyrosine
Let me introduce you one curious species. This is a little microorganism (archea), which lives in hot hydrotermal sources, and converts carbon dioxide into methane, with a remarkably lengthy name Methanocaldococcus jannaschii.
Same as we’re doing it, M jannaschii makes proteins by decoding RNA sequence into proteins. However, this is a fairly complex process overall. First an amino acid is recognized by a special enzyme, aminoacyl-tRNA-synthetase (AARS), the enzyme attaches the amino acid to a corresponding adaptor, the transfer RNA molecule (tRNA), and resulting conjugate, aminoacyl-tRNA then travels to the ribosome, where the amino acid will be incorporated in place of a correct codon. The identity of the amino acid is only checked by the the enzyme, AARS, and not checked thereafter. When you need to have tyrosine in a protein,special AARS will link tyrosine to corresponding tRNA, and this tRNA will then place the amino acid at the place of the tyrosine codons.
What’s so special about M. jannaschii though? Special is the fact that the tRNA for tyrosine in this organism is different to the tRNA of tyrosine in our best friend Escherichia coli. If we’d take this tRNA from M. jannaschii and transfer this to E. coli, the AARS from E. coli will not charge it with an amino acid. At this point we can make a good use of it. For example, we can charge this tRNA with something else, and E. coli will place this amino acid into a protein where we want to have it.
In the pair of AARS and tRNA, we can modify the amino acid recognition pocket of AARS such that it will accept another amino acid of interest, and then charge it on the tRNA, which will incorporate it into a protein on a position of a free codon (stop codon). Nether the synthethse, AARS, nor the tRNA from the M. jannschii is known for E. coli, and there will be no cross reactivity between different synthetases and tRNAs. The M. jannaschii pair of AARS and tRNA will act in parallel to the common cellular apparatus, therefore it is also called an orthogonal pair.
There is a number of orthogonal pairs originally used by different organisms for some amino acids. The system from the metanogenic microorganism M. jannaschii, is among the most common and reliable. To date, it has been used for incorporation of a huge set of chemically diverse structures into proteins in addition to the common set of 20 amino acids. Of course, most of these diverse structures are in some way resembling tyrosine or phenylalanine, because the original enzyme was for tyrosine. With O-propargoxy-tyrosine or para-azido-phenylalanine we will have a handle for click-chemistry, with para-cyano-phenylalanine we have a probe for infrared spectroscopy, with para-trifluoromethyl-phenylalanine - a probe for fluorine NMR, with O-ortho-nitrobenzyl-tyrosine (photocaged tyrosine) we will have a masked tyrosine residue, which can be set free by sheding light on it etc.
Why is tyrosine so useful in the protein structures? Well, it is reasonably hydrophobic, therefore it can be placed in the hydrophobic core. Nonetheless, even in the hydrophobic environments, it can make additional hydrogen bonds. There is an additional acid-base transition in the Tyr residue, the pKa of the phenolic group in Tyr is about 10, and this may be used for catalysis. The hydroxyl-group of Tyr can be phosphorylated and dephosphorylated for regulation purposes. As you can see, there are many reasons to have tyrosine in the genetic code.
One more fact should not be omitted. Tyrosine is a precursor for dopamine in our neurons. We all need it very much.
- Hubbard, S. R. and Till, J. H. Protein Tyrosine Kinase Structure and Function. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 69, 2000, 373-398, doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.69.1.373
- Wang, L. et al. Expanding the Genetic Code of Escherichia coli. Science, 292, 2001, 498-500, doi: 10.1126/science.1060077
- Radi, R. Nitric oxide, oxidants, and protein tyrosine nitration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 101, 2004, 4003-4008, doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307446101
Valine
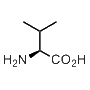
Valine is hydrophobic. Well, this is a true clear fact. But how hydrophobic could it get? Let’s try to understand.
When an amino acid is in a peptide sequence, the backbone would tend to folds into a particular conformation, and very importantly, the backbone is polar. How polar? Very polar, too damn polar, even too much. But it would fold into a conformation, and at the exterior there will be amino acid side chains. Remember, that the backbone is still very polar, and it would prefer to have contacts with surrounding water. The side chain can either allow or hinder these contacts. Because valine has a β-branched structure, it covers the backbone like an umbrella, and precludes contacts of the backbone to water. This is why a hydrophobic structure can be featured by valine even better than by leucine, despite the fact that valine is one carbon atom shorter.
There is another important outcome of the β-branched structure. Because the side-chain prevents solvation of the backbone, the backbone would like to change its conformation to regain contacts with the solvent. Thus, when valine is in the context of an ?-helix (compact structure, 1.5 Å per an amino acid residue), it can promote its isomerization into a β-strand (extended structure, 3 Å per an amino acid residue), and these can further associate into ?-sheets, and subsequently into amyloid fibrils. This is why valine is often regarded as ?-sheet promoting residue. However, one should understand the reason, why this conformation is promoted by valine, because the statement shouldn’t be generalized too much. The reason is clear differences in the backbone solvation. However, when isomerization occurs between β-strand and PPII helix, both featuring 3 Å per one amino acid residue, the solvation argument becomes more complicated, and in one context valine may preferentially form a PPII helix,* and oppose this conformation in another.
The conformational properties of valine are very important, and these play role in peptide design. For instance, by placing valines into a few or even one position in an β-helix, one can promote its isomerization into β-sheets, and subsequently build a model of amyloid formation.
* For example in GGXGG model sequences as reported by Shi, Z. et al. Polyproline II propensities from GGXGG peptides reveal an anticorrelation with β-sheet scales. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 102, 2005, 17964-17968, doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507124102
- Grling, U. I. M., et al. Concluding the Amyloid Formation Pathway of a Coiled-Coil-Based Peptide from the Size of the Critical Nucleus. ChemPhysChem, 16, 2015, 108-114, doi: 10.1002/cphc.201402400
A kinetic model for amyloid formation built through exchange of a few key positions in an β-helix into valine.
- Parent, A. et al. The B12-Radical SAM Enzyme PoyC Catalyzes Valine Cß-Methylation during Polytheonamide Biosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 138, 2016, 15515-15518, doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b06697
The paper discusses details of post-translational methylation of valine residues forming tert-leucine in polytheonamide.
- Lanza, G. and Chiacchio, M. A. Quantum Mechanics Study on Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Interactions in the Trivaline–Water System. J. Phys. Chem. B, 122, 2018, 4289-4298, doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b00833
The paper discusses how the backbone is solvated in trivaline peptides, when adopting ?-conformation and polyproline-II helix.